During the cooling process, we can identify three stages, as shown in the figure attached to the question.
1. Water cooling from 23°C to 0°C, freezing temperature of the water. The energy for this stage will be:
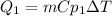
Where,
m is the mass of water, 250g
Cp1 is the specif heat of water, 4.186J/g°C
dT is the difference of temperature, T2-T1=0°C-23°C=-23°C
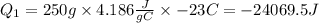
We have a negative value because the process releases energy
2. Change of phase of water, from liquid water to ice. This process occurs at a constant temperature equal to 0°C. The energy for this stage will be:
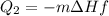
dHf is the heat of fusion. We put a negative sign because we have the contrary process of fusion, freezing.
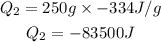
3. Ice cooling from 0°C to -23°C.
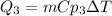
Where,
m is the mass of ice, 250g
Cp3 is the specific heat of ice, 2.1J/g°C
dT is the difference of temperature, -23°C-0°C=-23°C
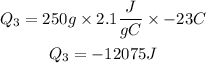
So, the total energy released will be:
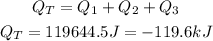
Answer: The total energy will be -119.6kJ, which means that the energy is released.