1) Write the chemical equation.
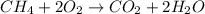
2) List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: CH4.
Volume: 2.0 L.
Temperature: 30 ºC = 303.15 K.
Pressure: 3.0 atm.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1).
Moles: unknown.
3) Moles of CH4.
3.1- Set the equation.
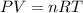
3.2- Plug in the known values and solve for n (moles).
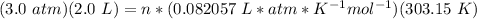
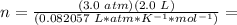
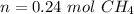
4) Moles of oxygen that reacted.
The molar ratio between CH4 and O2 is 1 mol CH4: 2 mol O2.
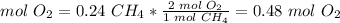
5) Volume of oxygen required.
Sample: O2.
Moles: 0.48 mol.
Temperature: 30 ºC = 303.15 K.
Pressure: 3.0 atm.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1).
Volume: unknown.
5.1- Set the equation.
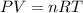
5.2- Plug in the known values and solve for V (liters).
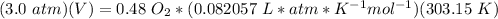
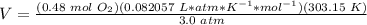
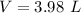
3.98 L of O2 is required to react with 2.0 L CH4.
.