2Pb(NO3)2(s) => 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
We have this reaction in a cylinder and also have 300 K. We are going to make some assumptions about these gases inside the cylinder: gases are ideal.
Then we will use this formula:
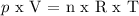
p = pressure in the cylinder
V = volume
n = moles
R = gas constant
T = temperature
Procedure:
1) We must calculate first how many moles we have after the decomposition of Pb(NO3)2, I mean how many moles of NO2(g) and O2(g) we have.
Note: PbO (s) takes up negligible volume (read the text please)
Let's calculate how many moles of Pb(NO3)2 is heated:
Moles Pb(NO3)2 = mass / molecular weight = 3.31 g / 331 g/mol = 0.01 moles
Using the reaction and stoichiometry we will calculate moles for NO2 and O2:
For NO2) 2Pb(NO3)2(s) => 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
2 moles Pb(NO3)2 --------- 4 moles NO2
0.01 moles Pb(NO3)2---------- x = 0.02 moles NO2
For O2) 2Pb(NO3)2(s) => 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
2 moles Pb(NO3)2----------- 1 mol O2
0.01 Pb(NO3)2 ------------ y = 0.005 moles O2
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2) Inside the cylinder we have:
Total moles = moles NO2 + moles O2 = 0.02 + 0.005 = 0.025 moles
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3) Using Ideal gas law and clearing the pressure:
V = 1.62 L
n = 0.025 moles
T = 300 K
R = 0.0820 atm x L / mol x K
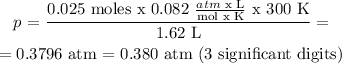
Answer: a) 0.380 atm