STak
Hello there. To solve this question, we'll have to remember some properties about exponential growth and solving exponential equations, inequalities.
Given the colonies A and B, for which the number of bacteria are, respectivelly, modelled by the equations:
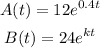
For t > 0 in hours. We have to determine:
a) The number of bacteria in colony A after 4 hours.
For this, we take t = 4 and calculate the following number:
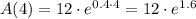
Using a calculator, we get the approximation:
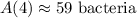
b) How long does it take for the number of bacteria in colony A to reach 400?
For this, we have to determine t such that:
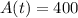
Hence plugging the exponential function, we get
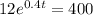
Divide both sides of the equation by a factor of 12
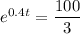
Take the natural logarithm on both sides of the equation
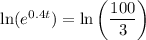
Apply the following property:
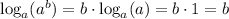
Knowing that:
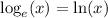
Hence we get:
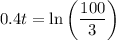
Multiply both sides of the equation by a factor of 2.5
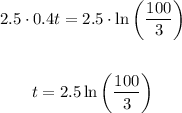
Using a calculator, we get the following approximation:
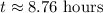
c) Find the value of k
For this, we have to use the fact that there are 60 bacteria in colony B after four hours;
Hence we get
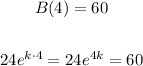
Divide both sides of the equation by a factor of 24
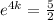
Taking the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation
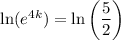
Applying the property presented before, we get
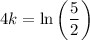
Divide both sides by a factor of 4
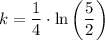
In this case it is better to keep the answer like this instead of using an approximaton.
With this, we have that B(t) will be
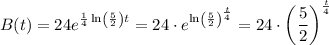
But we can keep it in the first form in order to solve part d).
d) The number of bacteria in colony A first exceeds the number of bacteria in colony B after n hours, where n is in integers. Find the value of n.
For this, we have to solve the following inequality:
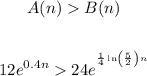
Since both exponential functions are powers of e and
We can solve the inequality without having to swap its order.
Divide both sides of the inequality by a factor of
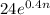
Hence we get
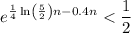
Since the logarithm is an one-to-one function, we take the natural logarithm on both sides of the inequality, preserving the order, therefore we get:
![\ln(e^{^{\left[(1)/(4)\ln\left((5)/(2)\right)-0.4\right]n}})<\ln((1)/(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ug8k0icoj9ca4kez0m6zl0zzf1y5mo93j9.png)
Applying the following property:
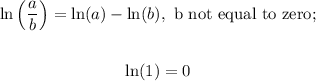
We get that
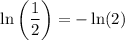
Hence we get by applying the very first property that
![\left[(1)/(4)\ln\left((5)/(2)\right)-0.4\right]n<-\ln(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/pmq2nm47zsv3rx9m5znmymltuzenw8fy8o.png)
Divide both sides by a factor of
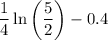
Notice it is a negative number, hence we swap the inequality sign as follows
![n\gt-\frac{\operatorname{\ln}(2)}{(1)/(4)\operatorname{\ln}\left((5)/(2)\right)-0.4}]()
Which evaluates to
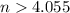
Since n is an integer, then we say
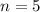
Is the first hour for which the number of bacteria on colony A exceeds the number of bacteria on colony B.