To find the derivatives we have to use the following property:
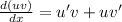
Then the first derivative will be:
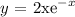
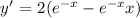
Now to find the second derivative we have to use the same derivative property with the part "-xe^-x. Thus:
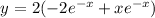
Now we have to equal the equation to zero:
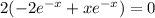
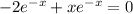

The first solution will be:
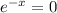
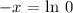
ln 0 is undefined, so this answer is impossible.
The second solution will be:
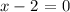
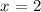
Answer: x = 2.