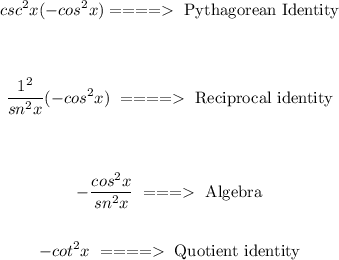
Given:
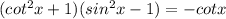
Let's verify the identity.
Apply Pythagorean identity on the left:
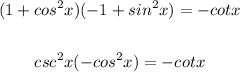
The next step is to apply reciprocal identity.
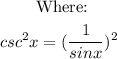
Thus, we have:
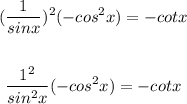
Solving further:
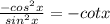
Apply quotient identity:
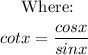
Using the quotient identity, we have:
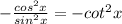
Therefore, the given equation is an identity.
We have the following: