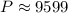You know that:
- She puts a population of 300 bacteria into a favorable growth medium at 8:00 A.M.
- At 5:00 P.M. the population is 1100 bacteria,
- The next morning, at 8:00 A.M. she comes back to the lab.
By definition, an Exponential Growth Model has the following form:
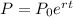
Where "r" is the growth rate (in decimal form), "t" is the number of times intervals and this is the initial amount:
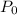
1. In this case, from 8:00 A.M to 5:00 P.M. you know that:
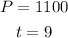
And the initial amount is:
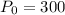
2. Then, you can substitute values into the equation and solve for "r", in order to find its value:
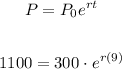
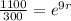
Remember the following properties:
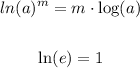
Then taking Natural Logarithm on both sides and simplifying, you get:
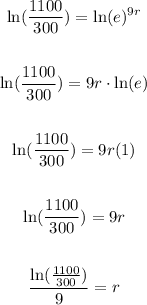
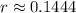
3. From 8:00 A.M. to 8:00 A.M in the next morning, there are 24 hours. Then, you can say that:
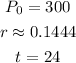
Now you can substitute values and find the number of bacteria at 8:00 A.M of the next morning:
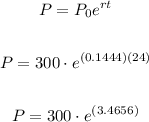
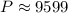
Hence, the answer is: