Answer
291.43mL
Step-by-step explanation
According to the combined gas law;
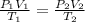
where:
• P₁ and P₂ are the, initial and final pressure, respectively
,
• V₁ and V₂ are the, initial and final volume, respectively
,
• T₁ and T₂ are the ,initial and final temperature, respectively (in Kelvin)
Given the following parameters
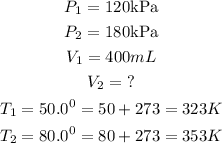
Substitute the given parameters into the formula to get the final volume V₂
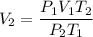
On substituting these values
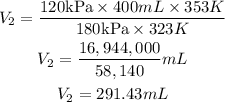
Hence its volume at a temperature of 80.0 °C and a pressure of 180 kPa is 291.43mL