Part A. We are given that a dart travels from rest to a velocity of 30 m/s with an acceleration of 330 m/s^2 to determine the time we will use the following equation of motion:
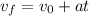
Where:
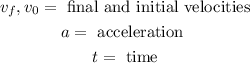
Since the dart is launched from rest this means that the initial velocity is zero, therefore:
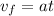
Now, we divide both sides by "a":
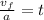
Now, we plug in the values:
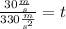
Solving the operation:
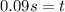
Part B. Now, we are asked to determine the distance. To do that we will use the following equation of motion:
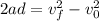
Now, we divide both sides by "2a":
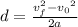
Now, we plug in the values:
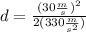
Solving the operations we get:
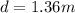
Therefore, the distance is 1.36 meters.