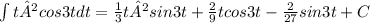Given the integral on the picture, we can use integration by parts to find the antiderivative.
First, let u = t² an dv = cos3t dt. If we find the derivative of u and the integral of v, we get:
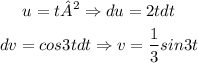
then, using the formula for integration by parts, we have the following:
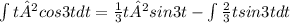
notice that the resulting integral on the right side also can be solved by parts. The solution of this integral is the following:
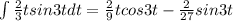
then, combining both results, we get: