Answer: We have to solve the following definite integral over a specified interval:
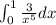
The solution steps are as follows:
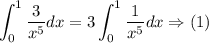
Applying the reverse power rule on the (1) gives the following answer:
![\begin{gathered} 3\int_0^1(1)/(x^5)dx=3[\int_0^1(1)/(x^5)dx=-(1)/(4x^4)] \\ \\ \\ \int_0^1(3)/(x^5)dx=[-(1)/(4x^4)]\rightarrow\text{ Evaluated at \lparen0,1\rparen} \\ \\ ----------------------- \\ -(1)/(4x^4)\rightarrow-(1)/(4(1)^4)-(-(1)/(4(0)^4)) \\ \\ \text{ Do note!} \\ (-(1)/(4(0)^4))\rightarrow\text{ Become infiniate} \\ \\ \text{ Therefore.} \\ \\ \\ -(1)/(4(1)^4)-(-(1)/(4(0)^4))=\text{ Diverges.} \\ \\ \text{ So the answer is:} \\ \\ \int_0^1(3)/(x^5)dx=\text{ Diverges} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/isfgy4pgyytbktthh1y3m3pq2mz1kxfd5c.png)
The integral therefore diverges.
The plot of the parent function clearly shows the behavior between (0,1)