Right Triangles
A right triangle is identified because it has an interior angle of 90° (right angle). The other two angles must be acute and add up to 90°.
In the special case that both acute angles have a measure of 45°, then we have an isosceles triangle, that is, both legs have the same length.
We can see one of the legs measures
![L=5\sqrt[]{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/o9ca8hdvtlv0sug0s8rtya1orezl6wg3xe.png)
Being this an isosceles triangle, the other leg (the base of the triangle) also measures L, thus you should drag
![5\sqrt[]{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8xvjn403qdbo7h1xksfr3a0v3r28mex0r3.png)
To the box at the bottom.
The other unknown length is the hypotenuse H. According to the Pythagorean's Theorem:
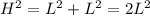
Substituting:
![\begin{gathered} H^2=2(5\sqrt[]{2}^{})^2 \\ \text{Operating:} \\ H^2=2\cdot50=10 \\ \text{Thus:} \\ H=\sqrt[]{100} \\ H=10 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/16l1rgd6eqjppo0xy105z88eebh9qic47z.png)
You should drag the length 10 to the hypotenuse.