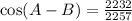Given that for positive acute angles A and B:
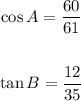
You need to remember that, by definition:
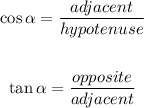
Look at the Right Triangle shown below:
It is also important to remember the following Trigonometric Identity:
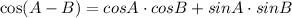
Then, in order to solve this exercise, you need to find:
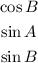
Using the data given in the exercise, you can draw these two Right Triangles (they are not drawn to scale):
Since by definition:
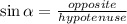
You need to find the opposite side of the first triangle and the hypotenuse of the second triangle. You can do this by applying the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that:
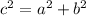
Where "c" is the hypotenuse, and "a" and "b" are the legs of the Right Triangle.
Then, the opposite side of the first triangle is:
![\begin{gathered} 61^2=60^2+b^2 \\ \\ 61^2-60^2=b^2 \\ \\ \sqrt[]{61^2-60^2}=b \\ \\ b=11 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/4c2m8xf45vf5n3a4yocre3wocemgz5jt4s.png)
And the hypotenuse of the second triangle is:
![\begin{gathered} c^2=12^2+35^2 \\ \\ c=\sqrt[]{12^2+35^2} \\ \\ c=37 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/2a289pwp6099ivwaea5xx5enco8ouamrwj.png)
Now you can determine that:
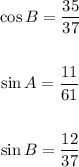
Substitute values into the Trigonometric Identity:
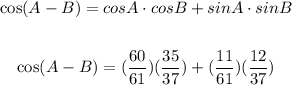
Simplify:
- Multiply the fractions:
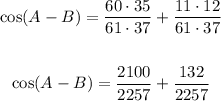
- Add the fractions:
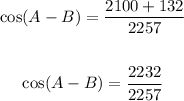
Hence, the answer is: