Answer:
2 x 10^(-5)
Step-by-step explanation:
The linear expansivity α can be calculated using the following equation:
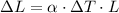
Where ΔL is the change in length, ΔT is the change in temperature and L is the original length of the metal. So, replacing the values, we get:
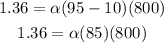
Then, solving for α, we get:
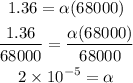
Therefore, the linear expansivity of the metal is 2 x 10^(-5)