F(x) = 1/2(x+3)(X-7)
Step 1 ; expand the function
F(x)= 1/2(x²-7x+3x-21)
F(x) = 1/2(x² - 4x-21)
F(x) = 1/2x² - 2x-21/2
Step 2 : Take the second derivative of F(x)
This means you are to differentiate F(X) twice
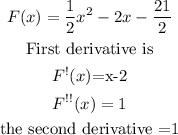
The second derivative is greater than 0, so it is a minimum point
Put x=1 in F(x) to find the value
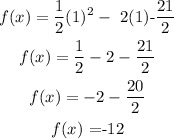
The minimum of the quadratic equation is -12