Given:
The volume of the gas, V=5.0 L
The temperature of the gas, T=251 K
The pressure of the gas, P=370 kPa
The gas constant, R=8.31 L kPa/(mol K)
To find:
The moles of the gas sample.
Step-by-step explanation:
From the ideal gas equation,
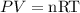
Where n is the moles of the gas present.
On substituting the known values,
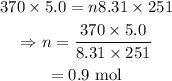
Final answer:
The moles of the gas present in the sample is 0.9 mol