The triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle. This means that each angle equals 60°. Hence, the angle at B is 60°.
The length of each side of ABC is given to be 3 cm long.
We can get the length of side AD by solving the triangle ABD using the Cosine Rule given to be:
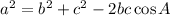
Since we're considering triangle ABD, and we have the measure of angle B, we can use the relationship:
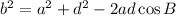
Note that a, b, and d are the sides, such that:
![\begin{gathered} a=BD=BC+CD=3+4=7\operatorname{cm} \\ b=AD \\ d=AB=3\operatorname{cm} \end{gathered}]()
Substituting these values, we have:
![\begin{gathered} AD^2=7^2+3^2-2(7*3*\cos 60) \\ AD^2=49+9-42\cos 60 \\ AD^2=37 \\ AD=\sqrt[]{37} \\ AD=6.08\operatorname{cm} \end{gathered}]()
The length of AD is 6.08 cm to 2 decimal places.