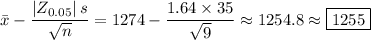I don't know what kind of calculator you have at your disposal, so I'll just give one way of computing the sample mean and standard deviation.
• To get the mean, add up all the data points and divide the total by the number of data:
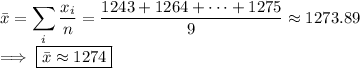
• To get the s.d. s, first compute the variance s² by adding up the squared difference between each of the data points and the sample mean, and divide the total by 1 less than the number of data:
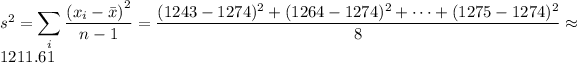
The s.d. is the square root of the variance:
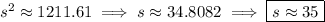
The 90% confidence interval for the sample mean has upper and lower limits, respectively, of
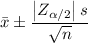
(positive root for upper limit, negative root for lower limit)
where
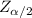 is the critical value for a (1 - α)×100% confidence level. By critical value, I mean
is the critical value for a (1 - α)×100% confidence level. By critical value, I mean
![\mathrm{Pr}\left[ Z \le Z_c \right] = c](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/5jta9tz1lpxo26sz38w3wyo71b04fv2l90.png)
where Z is a random variable following the standard normal distribution.
In this case, we have a 90% confidence level, so α = 0.1, and the critical value is
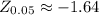 . Then the confidence interval has upper limit
. Then the confidence interval has upper limit
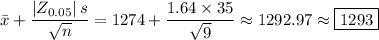
and lower limit