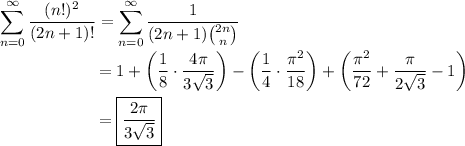Observe that
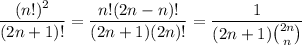
Starting with a well-known series
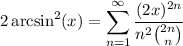
we take some (anti)derivatives to find a sum that more closely resembles ours.
Let
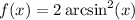 . Then
. Then
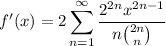
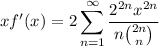
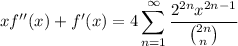
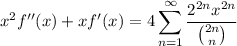
Noting that both sides go to zero as
 , by the fundamental theorem of calculus we have
, by the fundamental theorem of calculus we have
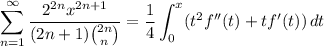
so that when
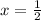 , and rearranging some factors and introducing a constant, we recover a useful sum.
, and rearranging some factors and introducing a constant, we recover a useful sum.
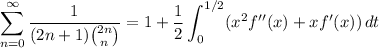
Integrate by parts.
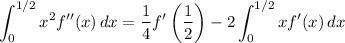
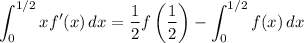
Then our sum is equivalent to
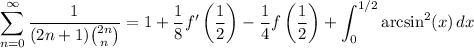
The remaining integral is fairly simple. Substitute and integrate by parts.
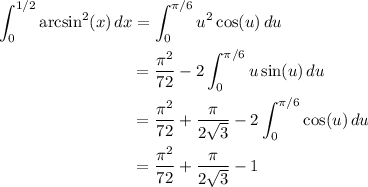
Together with
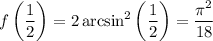
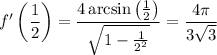
we conclude that