Given:
The vertices of the quadrilateral ABCD are A(3,8), B(6,5), C(5,4), and D(2,7).
To find:
Whether the given quadrilateral is a rectangle, a rhombus or a square.
Solution:
Distance formula: The distance between two points is
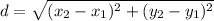
Using distance formula, the side lengths are:
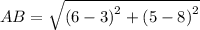
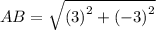
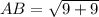
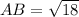
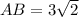
Similarly,
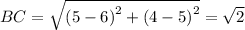
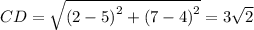
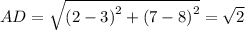
The length of diagonals are:
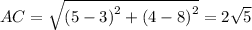
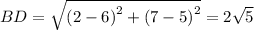
From the above calculation, we conclude that the given quadrilateral has two pairs of congruent opposite sides and equal diagonals.
Opposite sides of a rectangle are equal and its diagonals are also equal.
Therefore, the given quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle.