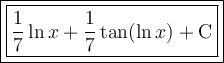Answer:
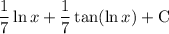
Explanation:
Given indefinite integral:
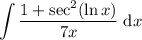
To integrate the given integral, we can use the method of substitution.
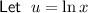
Differentiate u with respect to x:
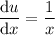
Rearrange to isolate dx:
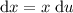
Rewrite the original integral in terms of u and du:
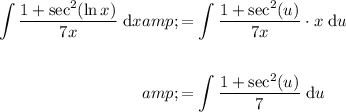
Take out the constant 1/7:
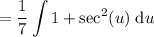
We can now evaluate the integral by using the following integration rules:

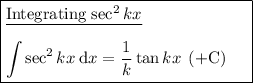
Therefore:
![\begin{aligned}\displaystyle (1)/(7)\int 1+\sec^2(u)\;\text{d}u&=(1)/(7)\left[u+\tan u]+\text{C}\\\\&=(1)/(7)u+(1)/(7)\tan u +\text{C}\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/mhox92f80d8b4clzcjse0qjcfz5nfcw0pu.png)
Substitute back u = ln x:
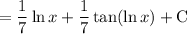
Therefore, the evaluation of the given integral is: