Answer:
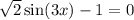
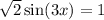
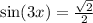
3x = π/4 + 2kπ or 3x = 3π/4 + 2kπ
x = π/12 + 2kπ/3 or x = π/4 + 2kπ/3
0 < π/12 + 2kπ/3 < 2π
0 < 1/12 + 2k/3 < 2
0 < 1 + 8k < 24
-1 < 8k < 23, so k = 0, 1, 2
x = π/12, 3π/4, 17π/12
0 < π/4 + 2kπ/3 < 2π
0 < 1/4 + 2k/3 < 2
0 < 3 + 8k < 24
-3 < 8k < 21, so k = 0, 1, 2
x = π/4, 11π/12, 19π/12