Final answer:
When aqueous solutions of iron(III) nitrate and sodium iodide are combined, a double replacement reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of insoluble iron(III) iodide, evidenced by a precipitation.
Step-by-step explanation:
When aqueous solutions of iron(III) nitrate and sodium iodide are mixed, a double replacement reaction occurs. This is because, based on solubility rules, the potential products, which are sodium nitrate and iron(III) iodide, may form. Sodium nitrate is soluble as all nitrates are, but iron(III) iodide is not soluble based on solubility rules for iodides when paired with certain metals like iron. Therefore, iron(III) iodide would precipitate out of the solution, confirming a chemical reaction has taken place.
The reaction can be represented by the ionic equation:
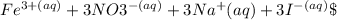 \(
\(
ightarrow\)
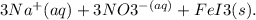 are spectator ions and do not participate in the reaction, showing that a precipitate of iron(III) iodide is indeed formed. This confirms that the correct answer is a double replacement reaction that results in the formation of an insoluble precipitate, making it also a precipitation reaction.
are spectator ions and do not participate in the reaction, showing that a precipitate of iron(III) iodide is indeed formed. This confirms that the correct answer is a double replacement reaction that results in the formation of an insoluble precipitate, making it also a precipitation reaction.