Answer: The volume needed at STP is 2.016 L
Step-by-step explanation:
According to avogadro's law, 1 mole of every substance occupies 22.4 L at STP and contains avogadro's number
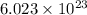 of particles.
of particles.
To calculate the moles, we use the equation:
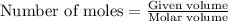
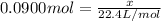
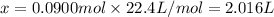
Thus the volume needed at STP is 2.016 L