Answer:
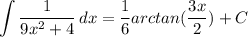
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra I
Calculus
Antiderivatives - integrals/Integration
Integration Constant C
U-Substitution
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
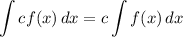
Trig Integration:
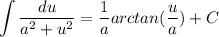
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
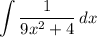
Step 2: Integrate Pt. 1
- [Integral] Factor fraction denominator:
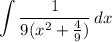
- [Integral] Integration Property - Multiplied Constant:
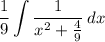
Step 3: Identify Variables
Set up u-substitution for the arctan trig integration.
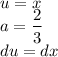
Step 4: Integrate Pt. 2
- [Integral] Substitute u-du:
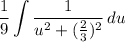
- [Integral] Trig Integration:
![\displaystyle (1)/(9)[(1)/((2)/(3))arctan((u)/((2)/(3)))] + C](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/u6k5w12xxgsrwmcaz6v7x7x93knn4oase9.png)
- [Integral] Simplify:
![\displaystyle (1)/(9)[(3)/(2)arctan((3u)/(2))] + C](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/gmivw8j5ym6d809tmj0ef2xhh04fovhkzi.png)
- [integral] Multiply:
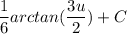
- [Integral] Back-Substitute:
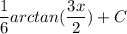
Topic: AP Calculus AB
Unit: Integrals - Arctrig
Book: College Calculus 10e