Final answer:
The maximum speed of electrons in an evacuated tube with an accelerating voltage of 40 kV is calculated non-relativistically by using the energy conservation principle. Equating the kinetic energy to the electrical potential energy, and solving the resulting equation using the charge and mass of an electron, allows for the determination of the electron's velocity.
Step-by-step explanation:
The student is asking about the maximum speed of electrons accelerated by an evacuated tube using a voltage of 40 kV. To calculate this non-relativistically, one can use the principle of conservation of energy where the kinetic energy (KE) gained by the electron is equal to the electric potential energy provided by the accelerating voltage.
The kinetic energy of the electron is given by KE = (1/2)mv^2, where m is the mass of the electron and v is the velocity of the electron. The potential energy (PE) is given by PE = eV, where e is the elementary charge and V is the accelerating voltage. By equating KE to PE, we can solve for v:
PE = KE
(1/2)mv^2 = eV
(1/2)mv^2 = (1.602 × 10-19 C)(40 × 103 V)
When solving for v, the resulting equation is:
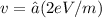
Plugging in the constants, the mass of an electron m = 9.109 × 10-31 kg, and the charge of an electron e = 1.602 × 10-19 C, we find:
![v = √[(2 × 1.602 × 10-19 C × 40 × 103 V) / (9.109 × 10-31 kg)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/engineering/college/rkgdszaz0ywyra08cx3u8byim792os6j3k.png)
This equation yields the maximum speed of the electrons accelerated by the evacuated tube.
The complete question is: evacuated tube method is what angle of insertion? is: