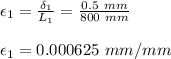Answer:
The answer is below
Step-by-step explanation:
The lengths of the rods are not given.
Let us assume the length of rod 1 = 1500 mm and the length of rod 2 = 800 mm
Solution:
The normal strain is defined as the change in member length δ divided by the initial member length L. The normal strain (ε) is:
ε = δ / L
δ = εL
For rod 1:
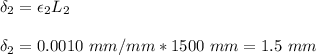
The axial elongation of rod 2 is 1.5 mm. Since rigid bar ABC is attached to rod 2, the rigid bar move down by same amount.
The rigid bar moves down 1.8 mm but rods 1 will not be stretched by this amount. Because there is a gap between rod (1) and the rigid bar at B, the first deflection of 1 mm would not cause an elongation in rod 1. Therefore, the elongation in rods (1) is:
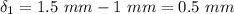
The normal strain in rod 1 is: