Answer:
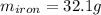
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the interaction between hot iron and cold water allows the heat transfer from iron to water and therefore we can write up the following energetic equation:
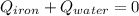
Whereas the heat terms can be written in terms of mass, specific heat and temperature change:
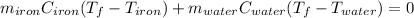
So we solve for the mass of iron as follows:
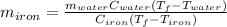
Now, we plug in the given data to obtain:
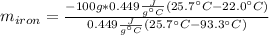
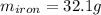
Best regards!