Answer:
3.56m due south
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Velocity of the car = 32m/s
Time = 9s
Unknown:
Displacement of the car = ?
Solution:
The velocity of a body is its displacement per unit of time in a specific direction.
Velocity =
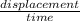
So;
Velocity =
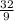 = 3.56m due south
= 3.56m due south