Answer:
Pythagorean theorem
Explanation:
We know that for a triangle if we know two sides and the included angle, the third side can be found out using cosine formula
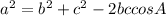
For a right angle triangle right angled at A this becomes
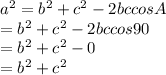
This is nothing but Pythagorean theorem