Hello!
Which equation is set up correctly to determine the volume of a 3.2 mole sample of oxygen gas at 50°C and 101.325 kPa?
We have the following data:
v (volume) = ? (in L)
n (number of mols) = 3.2 mol
T (temperature) = 50 ºC
First let's convert the temperature on the Kelvin scale, let's see:
TK = TºC + 273
TK = 50 + 273
TK = 323
P (pressure) = 101.325 kPa
R (gas constant) = 8.314 L . kPa/K.mol
We apply the data above to the Clapeyron equation (gas equation), let's see:
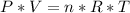
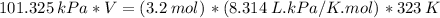
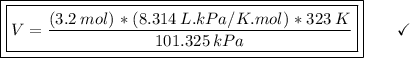
Answer:
(A) V=(3.2 mol)(8.314 L⋅kPa/K⋅mol)(323 K) / 101.325 kPa
________________________________
I Hope this helps, greetings ... Dexteright02! =)