Answer:
Pythagoras Theorem
Explanation:
For any triangle ABC, the law of cosine is given by

Now, let us suppose the triangle ABC is a right triangle having right angle at C.
Thus, C = 90°
Substituting this value in above formula
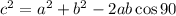
We know that cos 90°= 0
Thus, the equation becomes
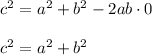
We can see that it reduces to Pythagoras Theorem.
Hence, we can conclude that law of cosines reduce to Pythagoras Theorem when dealing with a right triangle