Let F (n) denote the integral,
∫ x (1 - ln(x))ⁿ dx
We attempt to find a power-reduction formula for F (n) in terms of F (n - 1). Integrate by parts, with
u = (1 - ln(x))ⁿ → du = - n/x (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ dx
dv = x dx → v = 1/2 x ²
Then
F (n) = u v - ∫ v du
F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2 ∫ x (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ dx
F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2 F (n - 1)
From this relation, we get
F (n - 1) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n - 1)/2 F (n - 2)
F (n - 2) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻² + (n - 2)/2 F (n - 3)
F (n - 3) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻³ + (n - 3)/2 F (n - 4)
and so on, down to
F (1) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x)) + 1/2 F (0)
where
F (0) = ∫ x dx = 1/2 x ² + C
By recursively substituting, we find
→ F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2 [1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n - 1)/2 F (n - 2)]
… = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n (n - 1))/2² F (n - 2)
→ F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n (n - 1))/2² [1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻² + (n - 2)/2 F (n - 3)]
… = F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n (n - 1))/2³ x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻² + (n (n - 1) (n - 2))/2³ F (n - 3)
→ F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n (n - 1))/2³ x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻² + (n (n - 1) (n - 2))/2³ [1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻³ + (n - 3)/2 F (n - 4)]
… = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + (n (n - 1))/2³ x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻² + (n (n - 1) (n - 2))/2⁴ x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻³ + (n (n - 1) (n - 2) (n - 3))/2⁴ F (n - 4)
and so on, down to
F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + … + (n (n - 1) … 2 × 1)/2ⁿ F (0)
F (n) = 1/2 x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ + n/2² x ² (1 - ln(x))ⁿ ⁻¹ + … + (n (n - 1) … 2 × 1)/2ⁿ ⁺¹ x ² + C
We can write this more compactly as the sum,
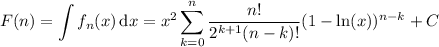
or
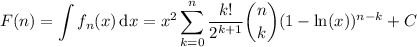
where
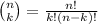 is the binomial coefficient.
is the binomial coefficient.