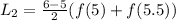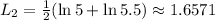Answer:
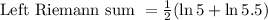
Explanation:
We are given y=ln(x)
We need to represent the left riemann sum with n=2
Please see the attachment for sketch and two left rectangle.
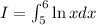
Left Riemann sum of integral
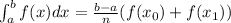
where, f(x)=ln(x), a=5 , b=6, n=2 ,
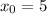 and
and

Now we write given integral into riemann sum