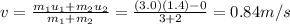Answer:
0.84 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
we can solve the problem by using the law of conservation of momentum: the initial momentum must be equal to the final momentum, so we can write
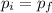
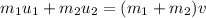
where
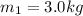 is the first mass
is the first mass
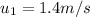 is the initial velocity of the first mass
is the initial velocity of the first mass
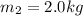 is the second mass
is the second mass
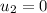 is the initial velocity of the second mass
is the initial velocity of the second mass
 is the final velocity of the two combined masses after the collision
is the final velocity of the two combined masses after the collision
Re-arranging the equation and substituting the numbers, we find