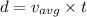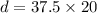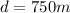Answer:
Part a)
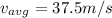
Part b)
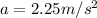
Part c)
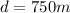
Step-by-step explanation:
Part a)
Since we know that bus is moving uniformly from initial speed of 15 m/s to 60 m/s in 20 seconds
So we will have
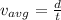
we know that
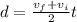
so we have
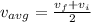
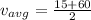
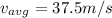
Part b)
As we know that acceleration is rate of change in velocity
so it is given as
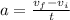
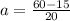
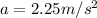
Part c)
distance moved by the bus is given as