To find the
hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) of this right triangle, we turn to one of the oldest and most renowned results in all of mathematics: the Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean Theorem states that the square of the legs of a right triangle is always equal to the square of its hypotenuse (leg²+leg²=hypotenuse²). Here, our legs our 4 and 5 respectively, and our hypotenuse is unknown. Let's call our hypotenuse
c. We have:
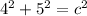
4² = 16, and 5² = 25, so putting the two together, we get:
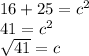
41 is prime, so we cannot reduce this radical any further. The measure of our hypotenuse c is √41.
For reference, and for its sheer elegance, I've included a copy of my favorite proof of the Pythagorean Theorem so you can get a feel for
why it works.