Vertical asymptote:
First, work out the domain of f(x).
The function is in form of algebraic fraction and it cannot be defined when the denominator is zero. The vertical asymptote is the same value of x that gives denominator = zero
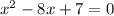
⇒ Factorize
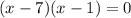
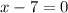
and

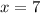
and
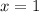
so, the vertical asymptote is at x = 1 and at x = 7
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Horizontal asymptote:
The three rules to determine the horizontal asymptote
1) The polynomial degree of numerator SMALLER to the polynomial degree of denominator, the horizontal asymptote is at y = 0 (along the x-axis)
2) The polynomial degree of numerator HIGHER than the polynomial degree of denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote
3) The polynomial degree of numerator EQUAL to the degree of the denominator, divide the coefficient of the highest degree term.
We have numerator = 3x³ - 28x² + 54x - 24 [this is a polynomial of degree 3]
We have denominator = x^2-8x+7 [this is polynomial of degree 2]
The polynomial degree of numerator > polynomial degree of the denominator, so there is no horizontal asymptote.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Slant asymptote:
Divide the numerator by the denominator
[3x³-28x²+54x-24] ÷ [x²-8x+7]
Refer to the diagram below
We have the result of 3x - 4 with a remainder
So the slant asymptote is 3x - 4