Answer:
Weight 16.6 g of KI, dissolve it in water, transfer to a volumetric ball of 100 mL and complete the volume with water.
Step-by-step explanation:
You must be careful with concentrations. First we have molarity, represented by a capital M, and then we have molality, represented by a lowercase m; they are defined next:
Molarity = M = moles of solute/ Liters of solution
Molality = m = moles of solute / Kg of solvent
if we were talking about molality, the problem wouldn’t be so easily resolve since they don´t give us the mass of solvent to be use but the volume of solution need and you will need the solution’s density to have an approximation of the mass solvent.
For this reason, I’m assuming we are talking about molarity. To solve the problem, we need to find the amount of KI we need to prepare the solution, for this we use the equation of molarity:
M = moles KI / Liters of solution
With this we can find the moles of KI needed:
Moles KI = M x liters of solution
Replacing the values:
Moles KI = 1.0 M x 0.1 L = 0.1 moles of KI
Note that 100 mL = 0.1 L. Now we need the grams of KI to be weighted. Using its molecular mass, which is 166 g/mol, we have:
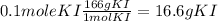
Then, we need to weight 16.6 g of KI, dissolve it in water (about 50 mL), transfer to a volumetric ball of 100 mL and complete the volume with water.