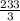ooh, fun
what I would do is to make it a piecewise function where the absolute value becomse 0
because if you graphed y=x^2+x-12, some part of the garph would be under the line
with y=|x^2+x-12|, that part under the line is flipped up
so we need to find that flipping point which is at y=0
solve x^2+x-12=0
(x-3)(x+4)=0
at x=-4 and x=3 are the flipping points
we have 2 functions, the regular and flipped one
the regular, we will call f(x), it is f(x)=x^2+x-12
the flipped one, we call g(x), it is g(x)=-(x^2+x-12) or -x^2-x+12
so we do the integeral of f(x) from x=5 to x=-4, plus the integral of g(x) from x=-4 to x=3, plus the integral of f(x) from x=3 to x=5
A.
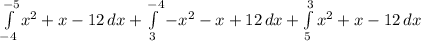
B.
sepearte the integrals
![\int\limits^(-5)_(-4) {x^2+x-12} \, dx = [(x^3)/(3)+(x^2)/(2)-12x]^(-5)_(-4)=((-125)/(3)+(25)/(2)+60)-((64)/(3)+8+48)=(23)/(6)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ec0i0tultszi8ah8bwq7yx4pjustjqjwsz.png)
next one
![\int\limits^(-4)_3 {-x^2-x+12} \, dx=-1[(x^3)/(3)+(x^2)/(2)-12x]^(-4)_(3)=-1((-64/3)+8+48)-(9+(9/2)-36))=(343)/(6)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9o2rfdinyoxxtz5rgc8v1vj815rhel74ty.png)
the last one you can do yourself, it is
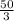
the sum is
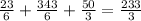
so the area under the curve is