Answer with Explanation
Let the polynomial function which is an odd function, be
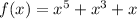
f(-x)= - f(x)
So,it is an odd function.
The function will pass through first and fourth quadrant.
Y intercept =0
Function is increasing in it's domain [-∞, ∞]
1. When f(x) becomes f(x)+2
g(x)=f(x) +2
This function will shift 2 units up, and it will not pass through the origin and has Y intercept equal to 2.
This function will also pass through first and fourth quadrant.
Function is an increasing function in it's domain [-∞, ∞]
Now, when f(x) becomes
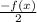
The function will pass through second and fourth Quadrant,due to negative sign before it, and distance from y axis either in second Quadrant or in fourth Quadrant increases by a value of
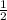 .
.
Here also, Y intercept =0
Function is a decreasing function in it's domain [-∞, ∞]
Now, taking the even function
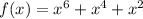
f(-x)= f(x)
So,it is an even function.
The function will pass through first and second quadrant equally spaced on both side of y axis.
Y intercept =0
Function is decreasing in [-∞,0) and increasing in (0, ∞]
1. When f(x) becomes f(x)+2
g(x)=f(x) +2
This function will shift 2 units up, and it will not pass through the origin and has Y intercept equal to 2.
This function will also pass through first and third quadrant.
Function is decreasing from [-∞,2) and increasing in (2, ∞]
Now, when f(x) becomes
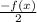
The function will pass through third and fourth Quadrant,due to negative sign before it, and function expands by the value of
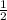 on both sides of Y axis.
on both sides of Y axis.
Here also, Y intercept =0
Function is increasing in [-∞,0) and decreasing in (0, ∞].