Answer:
The average rate of change from x = 2 to x = 3 is 2. Therefore first option is correct.
Explanation:
The average rate of a function f(x) on the interval [a,b] is defined as
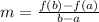
The average rate of change from x = 2 to x = 3 is
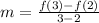 .... (1)
.... (1)
From the given graph it is clear that the value of the function is -3 at x=2 and -1 at x=3. It means f(2)=-3 and f(3)=-1.
Put f(2)=-3 and f(3)=-1 in equation (1).
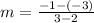
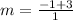
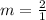
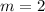
The average rate of change from x = 2 to x = 3 is 2. Therefore first option is correct.