Answer:
The density of nitrogen dioxide in a 3.50 L tank at 780.0 Torr and 37.0 °C is 1.86 g/L.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the density of gas, we use the equation given by ideal gas equation:
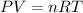
Number of moles (n)
can be written as:
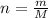
where, m = given mass
M = molar mass
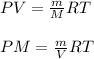
where,
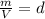 which is known as density of the gas
which is known as density of the gas
The relation becomes:
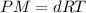 .....(1)
.....(1)
We are given:
M = molar mass of argon = 46 g/mol
R = Gas constant =
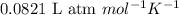
T = temperature of the gas =
![27.0^oC=[37.0+273]K=310 K](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/college/20ray5t6rbptwmv1y9tl2o6ef93is4w173.png)
P = pressure of the gas = 780.0 Torr=
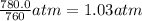
1 atm = 760 Torr
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
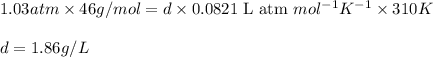
The density of nitrogen dioxide in a 3.50 L tank at 780.0 Torr and 37.0 °c is 1.86 g/L.