Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the information given:
The population size N = 5
The sample size n = 2
∴
without replacement; the number of possible samples;
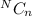
=
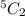
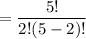
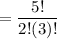
= 10
Thus, 10 different samples of 2 technicians each are possible.
DIfferent samples
S/No possible samples Mean
1 2 1 3/2 = 1.5
2 2 3 5/2 = 2.5
3 2 5 7/2 = 3.5
4 2 4 6/2 = 3
5 1 3 4/2 = 2
6 1 5 6/2 = 3
7 1 4 5/2 = 2.5
8 3 5 8/2 = 4
9 3 4 7/2 = 3.5
10 5 4 9/2 = 4.5
Total 30
Sample distribution for the sample mean
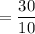
= 3
Population mean =
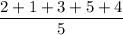
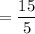
= 3
Thus, it is obvious that both means are equal