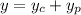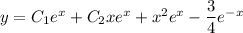First find the characteristic solution. The characteristic equation is
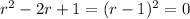
which as one root at
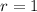
of multiplicity 2. This means the characteristic solution for this ODE is
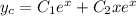
For the nonhomogeneous part, you can try a particular solution of the form
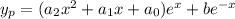
which has derivatives
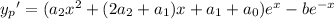
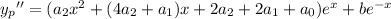
Substituting into the ODE, the left hand side reduces significantly to
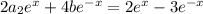
and it follows that
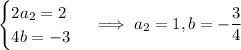
Therefore the particular solution is
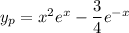
and so the general solution is the sum of the characteristic and particular solutions,