The Surface area of the prism is 222 square centimeters.
Let's break down the calculation of the surface area of the given prism step by step:
Step 1: Identify the Shapes Comprising the Base
The base of the prism is composed of three rectangles:
- Two side rectangles each with dimensions 5 cm by 3 cm.
- One middle rectangle on the top with dimensions 8 cm by 2 cm.
Step 2: Calculate the Area of Each Rectangle
- The area of each side rectangle is calculated by multiplying the length by the width:
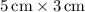 .
. - The area of the middle rectangle is calculated similarly:
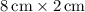 .
.
Step 3: Find the Total Base Area
The total base area is the sum of the areas of the three rectangles:
Total base area = Area of one side rectangle × 2 (because there are two identical side rectangles) + Area of the middle rectangle.
Step 4: Calculate the Perimeter of the Base
The perimeter of the base is the sum of all the sides of the rectangles that make up the outer edge of the base:
Perimeter base = (Length of one side rectangle + Width of the middle rectangle) × 2 + Length of the top rectangle × 2.
Step 5: Calculate the Surface Area of the Prism
The surface area of the prism is composed of the base area, the top area (which is equal to the base area), and the area of the sides (the perimeter of the base multiplied by the height of the prism):
Surface area = Base area × 2 + Perimeter of the base × Height of the prism.
Step 6: Perform the Calculations
- Area of one side rectangle:
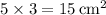 .
. - Area of the middle rectangle:
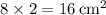 .
. - Total base area:
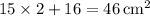 .
. - Perimeter of the base:
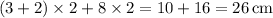 .
. - Surface area of the prism:
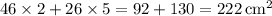 .
.
The answer is 222 square centimeters.