ASA congruence theorem: If two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
AAS congruence theorem: If two angles and the non-included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
Consider two triangles ΔABC and ΔA'B'C' . If AB=A'B', m∠A=m∠A' and m∠B=m∠B', then two triangles ΔABC and ΔA'B'C' are congruent by ASA theorem.
Now find ∠C and ∠C':

and
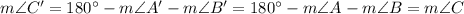
.
You have AB=A'B', m∠A=m∠A' , m∠C=m∠C' and that is the condition of AAS congruence theorem.
These thoughts show you that AAS theorem is straight extension of ASA theorem.