Answer and Step-by-step explanation: With the constant velocity motion formula, we can determine constant velocity of the object in motion whose data we collected:
x = x₀ + vt
Velocity can be calculated as:
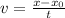
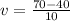
v = 3 m/s
The beginning of the data collect, object is 40m away, then x₀ = 40.
So, equation modeling the object's path is x = 40 + 3t.