"An acid is a substance that forms hydrogen ions when dissolved in water." this is an example of Arrhenius theory .
Explanation:
Any substance that, after ionisation, dissolves in liquid and produce hydrogen ions called Arrhenius acid (HCl, HCN,etc). Whereas, a substance that dissolves in aqueous releases hydroxide ions called Arrhenius base (NAOH, KOH, etc).
Arrhenius theory elaborates why acids have same properties: The internal properties of acids are determined by the presence of
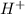 ions formed by dissolving acids in aqueous. These also explain why acid neutralises bases and vice versa. Acids give an
ions formed by dissolving acids in aqueous. These also explain why acid neutralises bases and vice versa. Acids give an
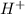 ion and the bases give an
ion and the bases give an
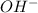 ions.
ions.
Example:
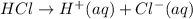
Where, (aq) stands for aqueous which means in the presence of water that is, water acts as a solvent.