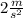Answer:
The bear's acceleration is
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnitude of the acceleration can be calculated using the following equation :
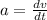 (I)
(I)
Where ''a'' is the acceleration
Where ''dv'' is the speed variation
Where ''dt'' is the time variation
In this exercise, the time variation is equal to 3 seconds because it is the amount of time in which the bear accelerated from
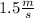 to
to
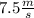
The speed variation is equal to :
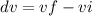
Where ''vf'' is the final speed and ''vi'' is the initial speed.
Finally, we can calculate the bear's acceleration using the equation (I) :
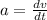
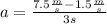
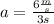
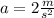
We find that the bear's acceleration is